Planning Your Astrophotography Shoot: Understanding Moon Phases and Light Pollution
Astrophotography is an awe-inspiring pursuit that allows us to capture the beauty of the cosmos through intricately detailed images of the night sky. But creating stellar astrophotography isn’t just about having a good camera and pointing it upwards. Mastering this art form requires a strategic approach, which involves understanding the celestial elements that influence the quality of your photos – namely, moon phases and light pollution. This comprehensive guide is tailored to the astrophotography enthusiast or photography hobbyist who wants to enhance their shots, optimize conditions, and reveal the universe in its full glory.

The Moon’s Influence on Night Photography
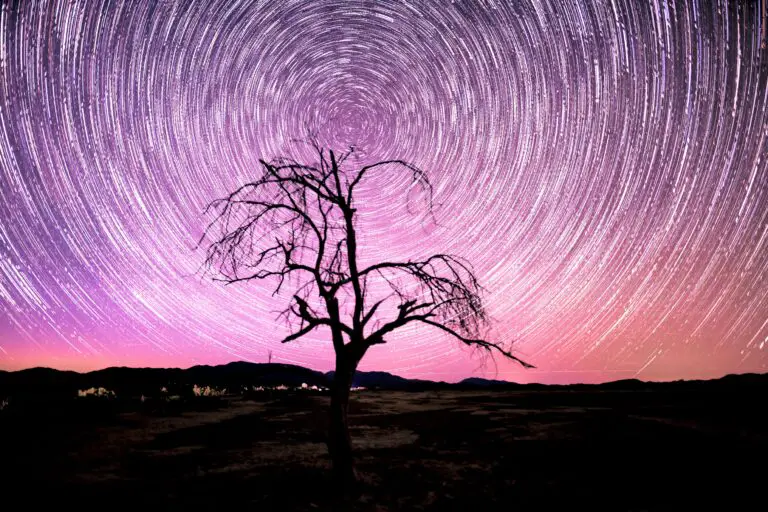
The moon is a powerful presence in the nocturnal canvas, and its phases affect the surrounding sky dramatically. For the astrophotographer, moon phases are crucial in determining the amount of natural light that will accompany your star shots and how it can be harnessed to your advantage.
New Moon: A Blessing of Darkness
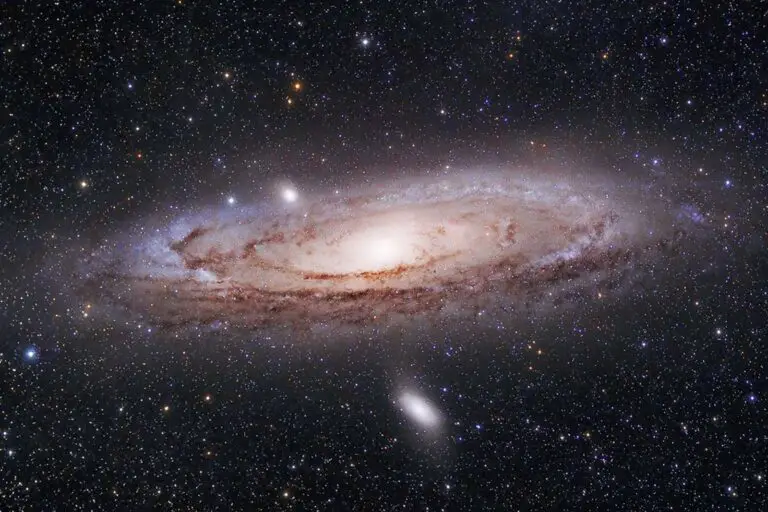
During the new moon phase, the moon’s dark side is facing directly away from Earth, which means the night sky is at its darkest. This is the ideal condition for capturing galaxies, nebulae, and other deep-sky objects clearly, as you experience minimal interference from moonlight. However, shooting during a new moon also means that the sky is devoid of the moon’s ambient light, which can create dramatic and stark silhouettes.
Full Moon: The Double-Edged Sword
A full moon can be a hinderance or a creative boon. While the significant luminance of a full moon can illuminate landscapes and foreground objects, providing a unique Earth-sky contrast, it can also wash out the subtler details of the Milky Way or dimmer objects. The trick to shooting under a full moon is to plan compositions that incorporate its light effectively, or focus on celestial subjects that can stand out against it.
Phases In Between: Finding Balance
The lunar cycle moves through waxing and waning states as it approaches the full and new moon. For astrophotography, these intermediate phases offer varying degrees of moonlight – enough to assist with low-light conditions, but not so much as to overpower the stars. These periods can provide a more balanced illumination, which can be particularly advantageous for landscape astrophotography.
Navigating Light Pollution
In the modern world, light pollution poses a significant challenge to astrophotography, as it brightens the sky and reduces visibility of stars and faint celestial objects. Understanding its impact and mitigating strategies are essential to successful night photography.
The Impact of Artificial Light
Light pollution refers to the excessive and misdirected artificial light that brightens the night sky. Streetlights, building lights, and other urban sources can create a glowing sky dome, which not only dims stars but also affects image contrast and color accuracy. The severity of light pollution can be determined using a Bortle Scale, with Class 1 being the darkest skies and Class 9 representing the most severe light pollution.
Seeking the Darkness
The best photos are often taken in the darkest locations. Identifying and heading to dark sky locations – such as designated “Dark Sky Parks” or remote rural areas – can provide the best opportunities for clear celestial sightings. Tools like light pollution maps can help you scout for spots that offer the darkness needed for your shoot.
Filters and Techniques to Combat Glow
Light pollution filters, such as the renowned “Astronomik CLS” or “Hutech IDAS,” can be used to selectively block the most common types of artificial light, allowing for a clearer view of the night sky. Additionally, post-processing techniques, such as gradient filters or pixel math in astrophotography software, can help minimize the effects of light pollution in your images.
Tips for Planning Your Astrophotography Shoot
Preparation is the key to success, especially when the unpredictable factors of weather and celestial events are involved. Here are some tips to help you meticulously plan your next astrophotography session.
Weather Watch
Keep a close eye on the weather forecast leading up to your shoot. Clear, cloudless skies are a must for astrophotography. Utilize apps and websites that offer detailed night sky forecasts to ensure you make the most out of your preferred shooting window.
Pack the Right Gear
Preparing your equipment is more than just ensuring you have everything. It’s about readying your camera, testing its settings, and making sure every item in your gear bag serves a purpose. Key items include a sturdy tripod, a wide-angle lens with a low f-stop, backup batteries, and memory cards. Don’t forget extra layers and provisions for you, the photographer!
Timing Is Everything
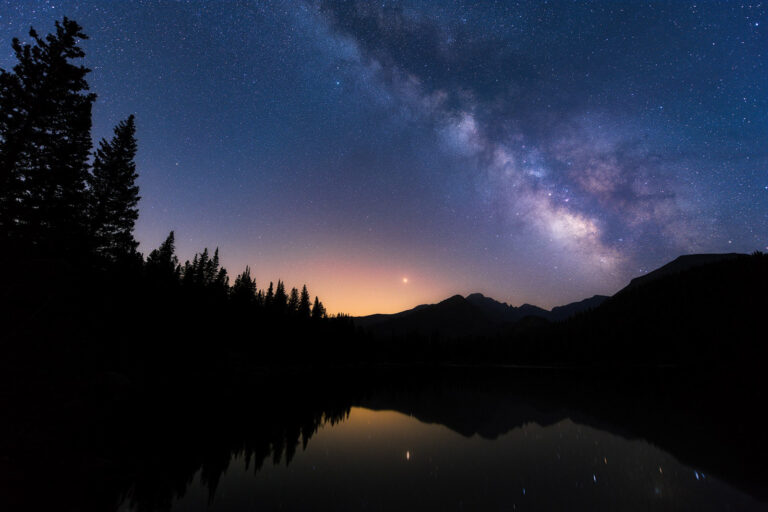
Selecting the right time to shoot is crucial. For instance, aiming for the galactic center of the Milky Way during its peak visibility can result in the most stunning photos. Plan your shoot according to the position and visibility of celestial objects, and the balance of moonlight for the kind of shots you wish to capture.
Location, Location, Location
Choose your shooting location wisely. Ensure it offers the desired level of darkness, safety, and an interesting foreground that can complement your celestial subject. Visit the location during the day to scout for potential compositions, and familiarize yourself with the environment’s natural and artificial light sources.
Showcasing Your Results
Beautiful photographs are meant to be shared. Learn how to enhance your astrophotography and find your place in the community of stargazing photographers.
Edit with Precision
Advanced photo editing software, like Adobe Lightroom and Photoshop, will be your best friends when sharpening, adjusting the exposure, and fine-tuning your astrophotographs. Post-processing not only corrects for the issues like light pollution but can also dramatically improve the visibility and details of celestial bodies.
Online Sharing Strategies
Strategically sharing your work on social media platforms and astrophotography forums can connect you with other enthusiasts, receive constructive feedback, and even garner attention from the community. Tagging your images with relevant astronomy hashtags can also help to expand your reach.
Building a Community
Consider starting a photography blog, joining astrophotography groups, or even participating in local or online astrophotography events. Building a network of like-minded individuals can provide learning opportunities, inspiration, and a sense of community that fuels the passion for astrophotography.
Conclusion
By understanding and planning around the moon’s phases and light pollution, you can significantly improve the quality of your astrophotography. Armed with this knowledge, your next shoot will be a well-executed endeavor that captures the wonder of the universe and pushes the boundaries of your creativity and skill as a photographer. Remember, the universe is vast and dynamic, offering a constellation of opportunities to photograph the night sky. Start planning, keep learning, and enjoy the celestial dance that you capture through your lens.